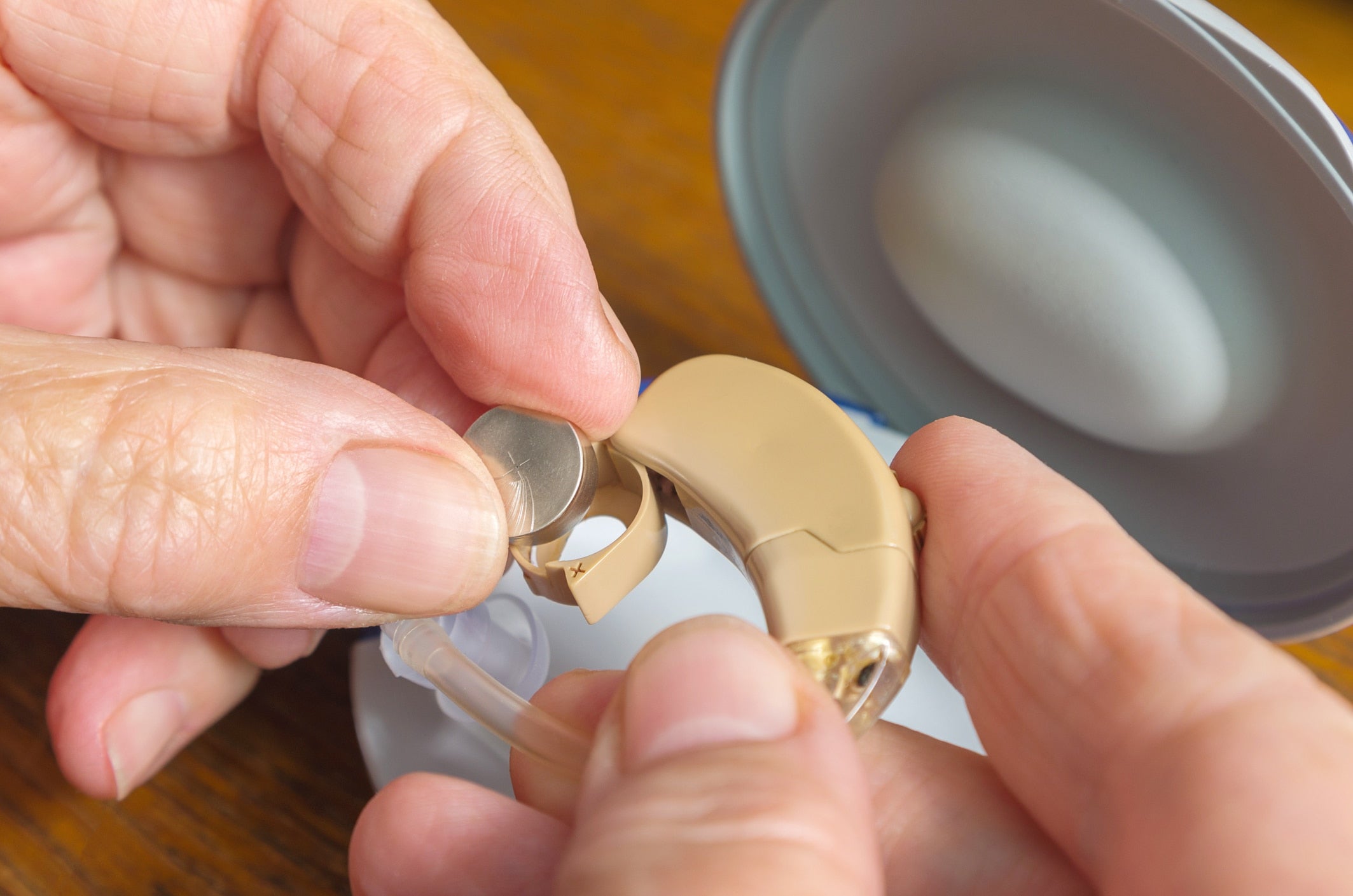
Knowing when to replace a hearing aid battery is essential for sound quality, reliability, and daily comfort. A weak or dying battery can make hearing aids sound distorted, cut out unexpectedly, or stop working altogether—often at the worst possible moment.
This guide answers the most common questions in a clear Q&A format, covering warning signs, battery life by type, and best practices for U.S. hearing aid users.
Q1: When should I replace my hearing aid battery?
You should replace your hearing aid battery as soon as you notice reduced performance or receive a low-battery alert.
Common indicators include:
-
Sound becomes weak, muffled, or distorted
-
Hearing aids cut in and out
-
You hear warning beeps or tones
-
The device shuts off unexpectedly
-
Rechargeable hearing aids don’t last a full day
Waiting too long can cause missed conversations, listening fatigue, and unnecessary stress.
Q2: How often do hearing aid batteries need to be replaced?
It depends on the battery type and hearing aid usage.
Disposable hearing aid batteries:
-
Size 10: every 3–5 days
-
Size 312: every 5–7 days
-
Size 13: every 7–10 days
-
Size 675: every 10–14 days
Rechargeable hearing aid batteries:
-
Recharge daily
-
Replace the internal battery every 3–5 years (depending on model and usage)
Streaming audio, phone calls, and noisy environments can shorten battery life.
Q3: What are the most common signs a hearing aid battery is dying?
Typical warning signs include:
-
Sudden drop in volume
-
Crackling or static sounds
-
Intermittent sound loss
-
Hearing aids turning off and back on
-
Shortened daily usage time
Many modern hearing aids also play audible low-battery alerts or send notifications through a smartphone app.
Q4: Should I replace the battery immediately after a low-battery alert?
Yes. Once you hear a low-battery alert, you typically have:
-
30 minutes to a few hours of use left (varies by device)
Because remaining time is unpredictable, it’s best to replace the battery as soon as possible, especially before:
-
Leaving home
-
Attending meetings or social events
-
Driving or traveling
Q5: Is it okay to wait until my hearing aid stops working to replace the battery?
It’s not recommended.
Waiting until the battery is completely dead can:
-
Interrupt conversations
-
Cause frustration or safety issues
-
Increase listening effort and fatigue
Proactive replacement ensures consistent sound quality and reduces daily disruptions.
Q6: How do I know which battery size my hearing aid uses?
Hearing aid battery sizes are color-coded in the U.S.:
-
Yellow: Size 10
-
Brown: Size 312
-
Orange: Size 13
-
Blue: Size 675
You can also check:
-
Your hearing aid manual
-
The battery door
-
Packaging from previous batteries
Using the correct size is critical—never force a battery into the device.
Q7: Do rechargeable hearing aids still need battery replacement?
Yes, but less frequently.
Rechargeable hearing aids:
-
Are charged daily
-
Use built-in lithium-ion batteries
-
Typically need battery replacement after 3–5 years
If your rechargeable hearing aid no longer lasts a full day—even after a full charge—it may be time for a battery replacement or device upgrade.
Q8: Can battery problems damage my hearing aids?
Yes, in some cases.
Potential risks include:
-
Battery leakage damaging internal components
-
Corrosion from expired or damaged batteries
-
Power fluctuations affecting sound processing
Always remove batteries if:
-
You won’t use your hearing aids for several days
-
The device gets wet
-
A disposable battery looks swollen or corroded
Q9: How can I make hearing aid batteries last longer?
To extend battery life:
-
Open the battery door when not in use
-
Store batteries at room temperature
-
Remove the sticker and wait 1–2 minutes before inserting (for zinc-air batteries)
-
Reduce unnecessary Bluetooth streaming
-
Turn off hearing aids when not needed
For rechargeable models, avoid overexposure to heat and charge them overnight using the manufacturer’s charger.
Q10: Do hearing aid batteries expire?
Yes.
Disposable hearing aid batteries typically expire 2–4 years after manufacture. Expired batteries may:
-
Drain faster
-
Provide inconsistent power
-
Leak and damage devices
Always check the expiration date on the battery package before use.
Q11: Is it normal for one hearing aid battery to die faster than the other?
Yes, especially if:
-
One hearing aid streams more audio
-
One ear has higher amplification needs
-
Bluetooth or microphone usage differs
However, a large or sudden difference may indicate:
-
A device issue
-
Moisture or wax buildup
-
A faulty battery
If the problem persists, professional servicing is recommended.
Q12: How often should I replace batteries for safety and reliability?
A good rule of thumb:
-
Disposable batteries: replace every few days based on size and usage
-
Rechargeable hearing aids: charge daily, replace internal batteries every few years
Many users choose to replace disposable batteries on a fixed schedule (for example, every Sunday) to avoid unexpected shutdowns.
Q13: Does replacing the battery affect hearing aid settings?
No. Replacing the battery does not erase programming or settings.
Your hearing aid settings are stored internally and remain unchanged when:
-
You replace disposable batteries
-
The rechargeable battery is recharged
If settings seem different after a battery change, the issue is likely related to power level or device condition—not data loss.
Q14: What’s the bottom line on when to replace a hearing aid battery?
Key takeaways:
-
Replace the battery at the first sign of low power
-
Don’t wait for the device to shut off completely
-
Disposable batteries last 3–14 days, depending on size
-
Rechargeable batteries last 3–5 years before replacement
-
Proactive replacement improves sound quality and reliability
A fresh battery ensures your hearing aids perform at their best—so you don’t miss important moments, conversations, or sounds.




Compartir:
How Long Do Hearing Aids Last?
Common Hearing Aid Problems and How to Fix Them